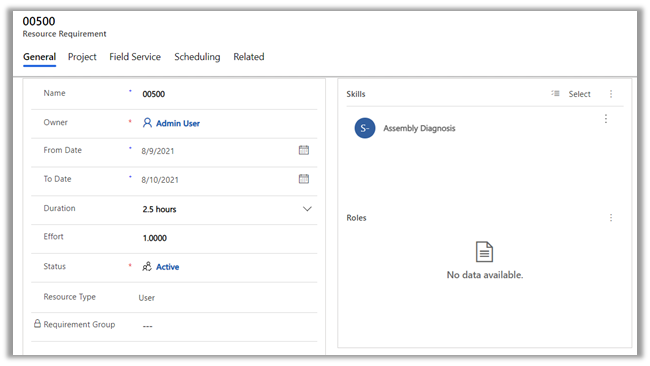
Let us have a look at the different options provided in the Email Tab for Tracking and Automatic creation of records.
Also check – https://crmkeeper.com/2020/04/20/dynamics-365-queue-setup-with-shared-mailbox/
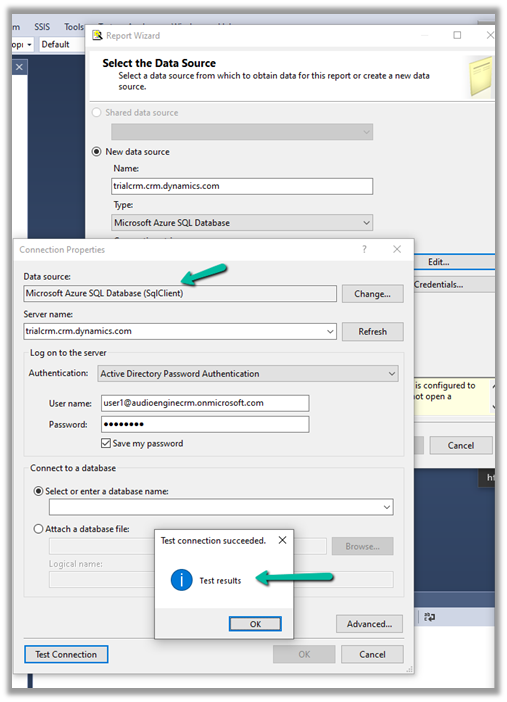
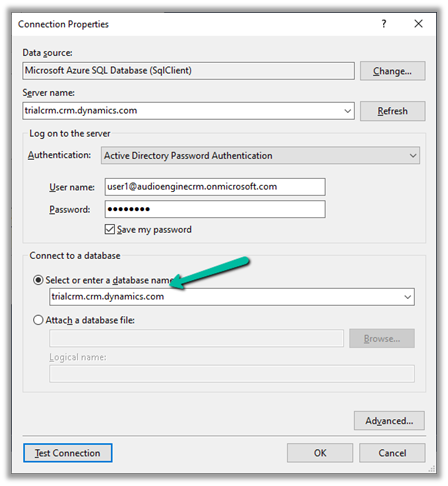
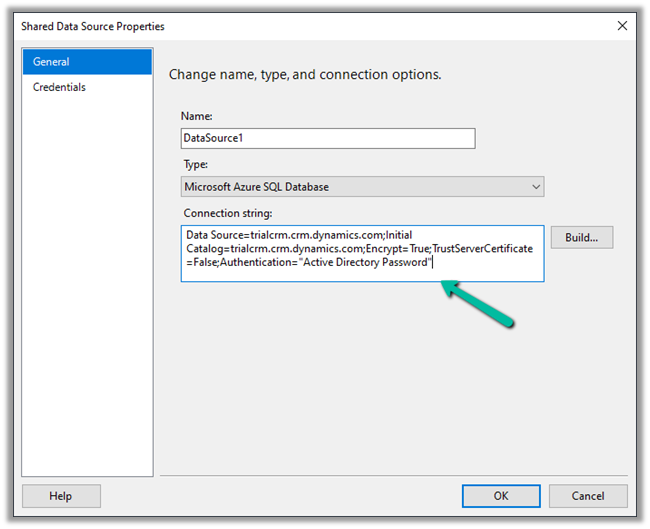
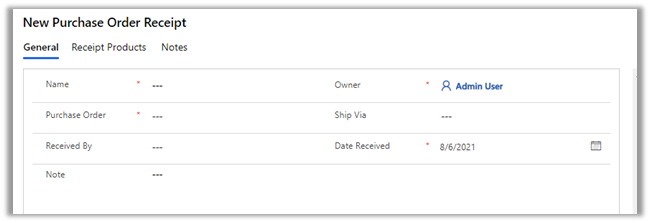
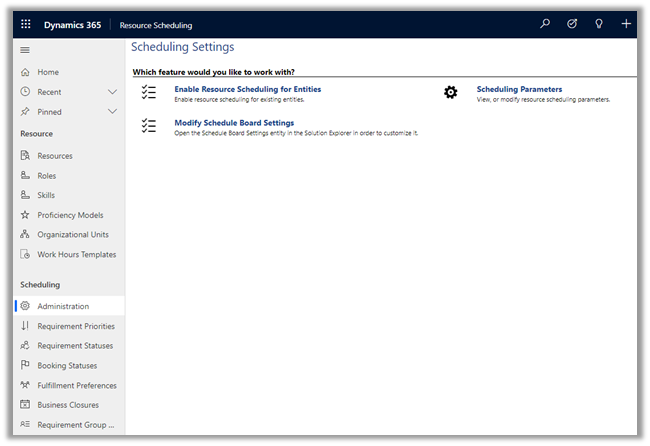
Select Personalization Settings in the Settings icon within the app.
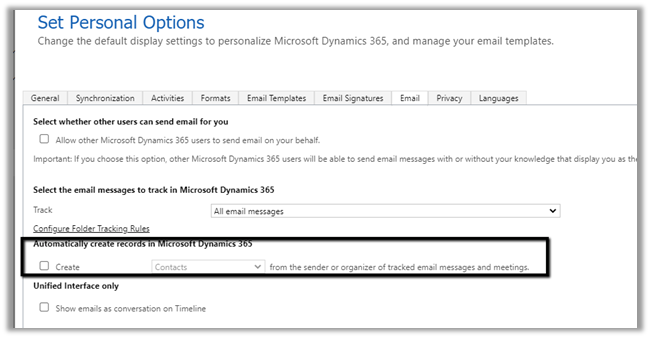
Select Email tab within Set Personal Options Dialog box.
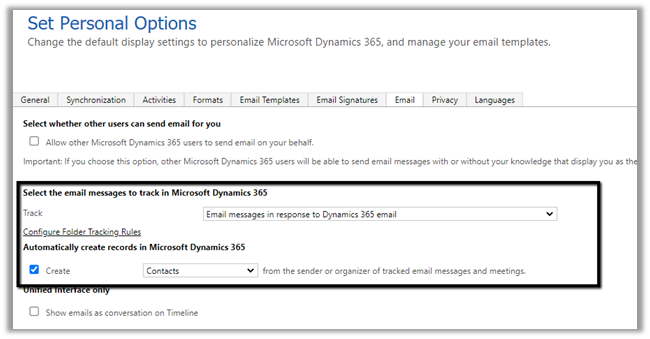
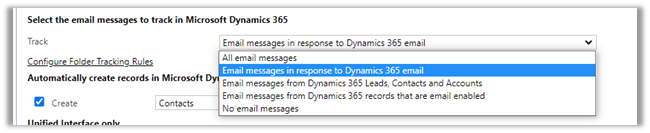
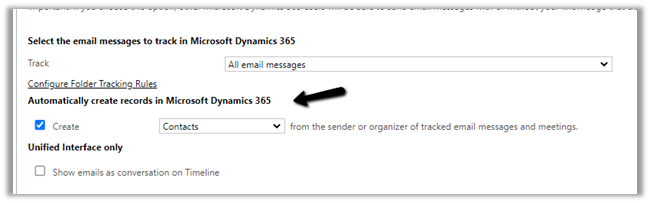
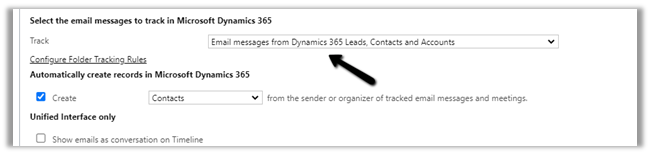
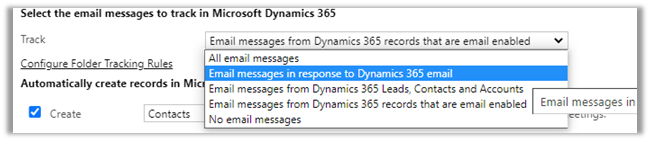
Select the email messages to track in Microsoft Dynamics 365 option has the following values
Email messages in response to Dynamics 365
email is the default option.
Let us start with the All email messages option.
- All email messages – In the case of all email messages, all email messages will be tracked in Dynamics 365, including the junk mail.

Here we have sent a test email to the CRM User with Track All email messages selected
The CRM user has his mailbox already configured.
Sample mail sent to the CRM user from the personal Hotmail account.
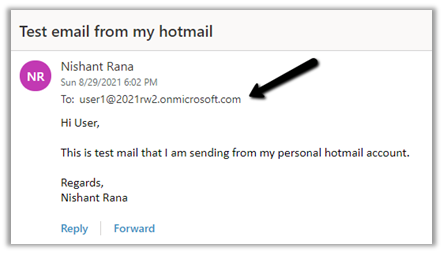
Inside Outlook Office, we can see the same mail received and marked as Tracked to Dynamics 365.
And an email activity created inside CRM.
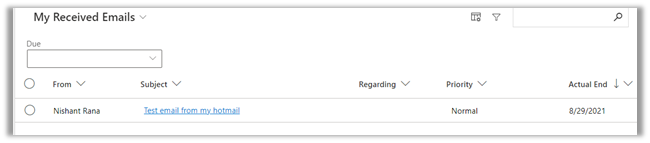
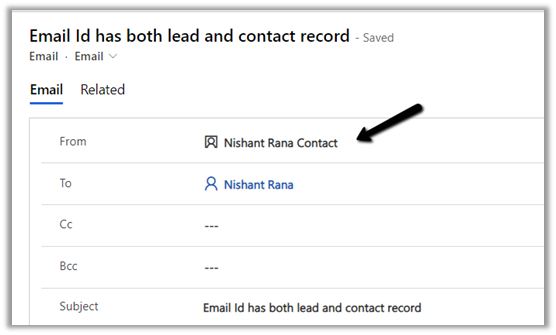
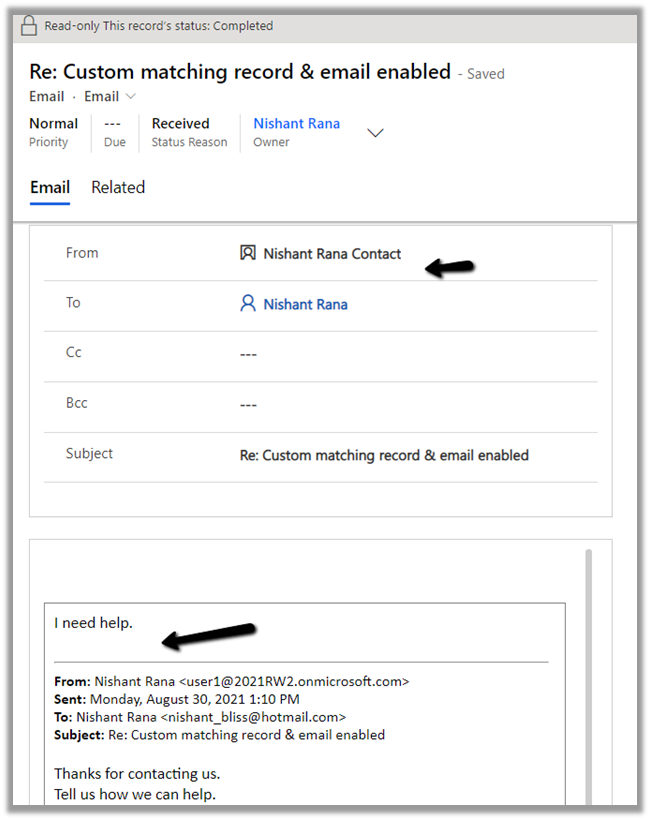
We can see the existing contact record having the matching email id being set as from for the email.
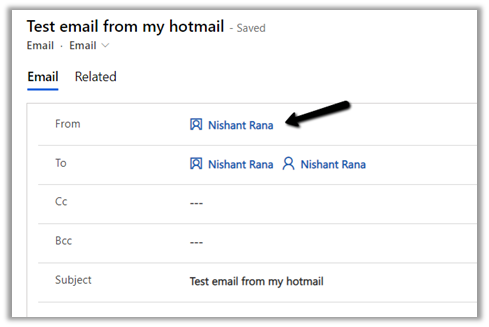
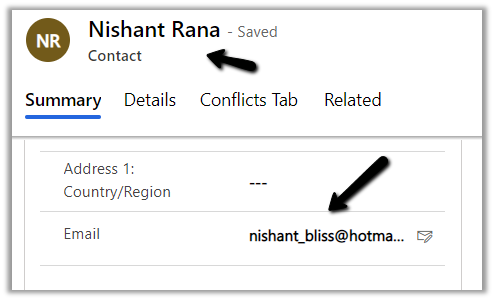
If no contact record is found with the same email id, then a new contact record will be created for the tracked email, if the below setting “automatically create record” is enabled.
Here I am now sending an email to the CRM user through my Gmail id. (This email id doesn’t exist in CRM for any records)

We can see the mail tracked, and the email activity created along with the new contact record.

Let us just disable create record option and also delete the existing contact records (both Hotmail and Gmail) with matching email id, so that no match is found.
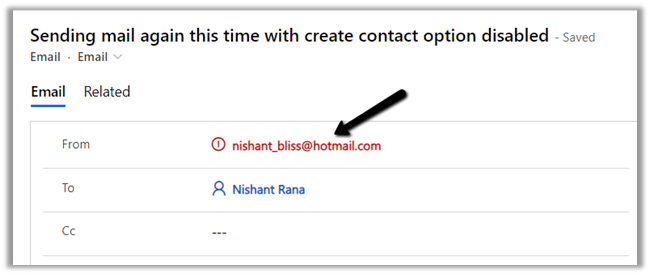
Let us again send an email from the Hotmail account to the CRM user
This time in the email activity created, we see the email id marked as red as there were no matching records in CRM.
Also as we had disabled contact creation so no contact record was created.
- What if we enable Lead Creation instead?
Remember we still do not have any existing matching contacts in CRM as we have deleted them.
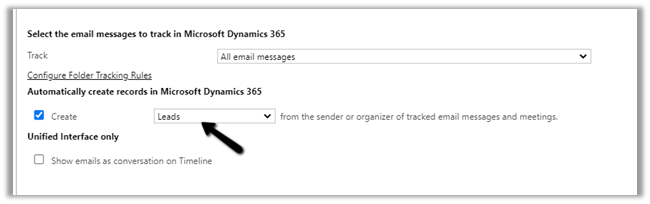
Let us sent a test mail and check.
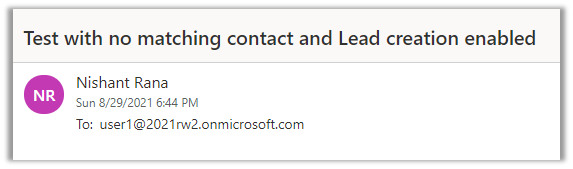
The email activity inside CRM will have the From part set as the lead record created as part of tracking.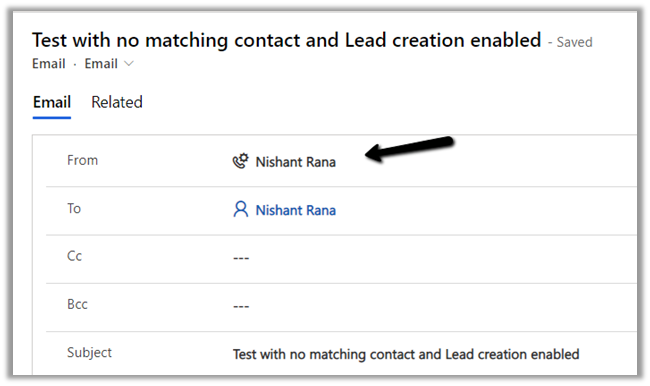
Below is the lead record created with associated email
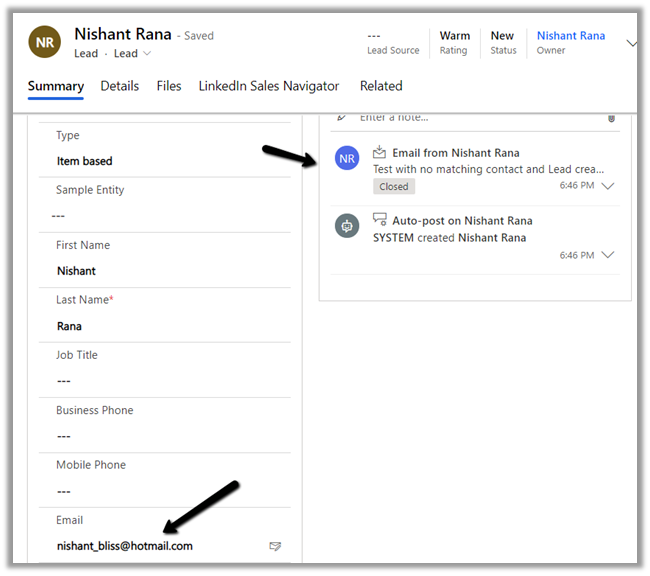
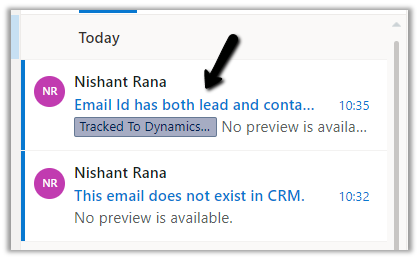
- What if we have both lead and contact records with the matching email id, to which record will the tracked email be associated?
The answer is the contact record.
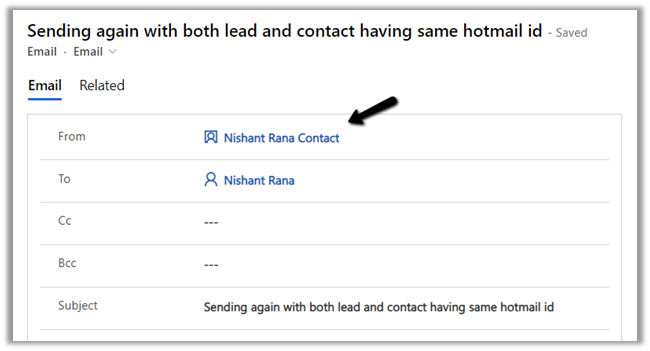
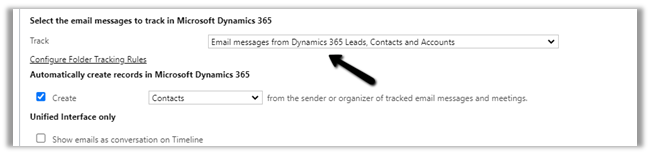
- Now let us look at the other tracking option – Email messages from Dynamics 365 Leads, Contacts, and Accounts – In this case only if the email is originated from the user having an existing lead, contact, or account record will be tracked.
- Let us send an email from an account that doesn’t have any lead, contact, or account record created inside CRM.
And also email from an account that has both lead and contact records.
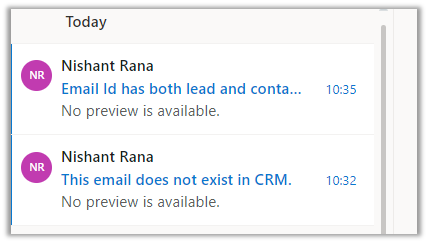
After a couple of minutes, we can see the mail from the account having lead and contact records being tracked and the other email from an account that doesn’t have any matching records not being tracked.
The email activity is associated with the contact record as expected.
- Now let us send the mail from an account with matching lead and contact, this time we have disabled the matching contact record.
So now the system has only a matching lead record.
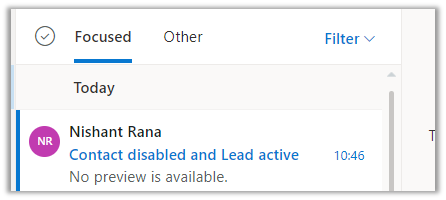
We have disabled the matching contact record.
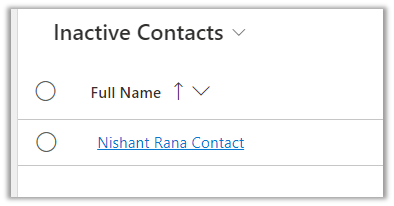
Result – We can see the email activity associated with the lead in this case as the contact was disabled.
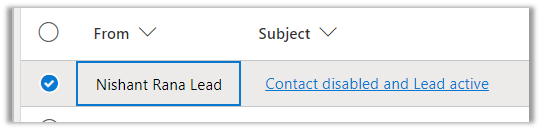
- Now let us disable and both matching lead and contact see the result.
And create one more custom entity record with email enabled having matching email id.
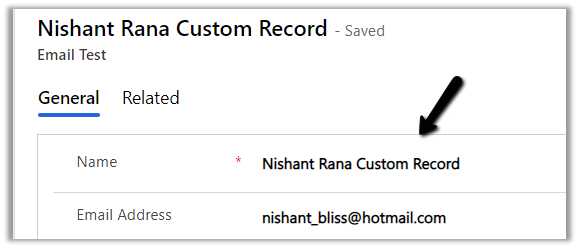
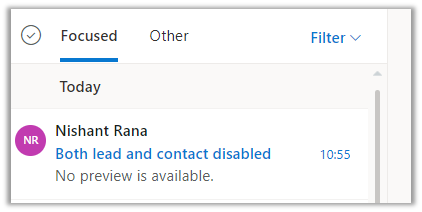
In this case, the email activity is associated with an active custom entity record having the matching email id
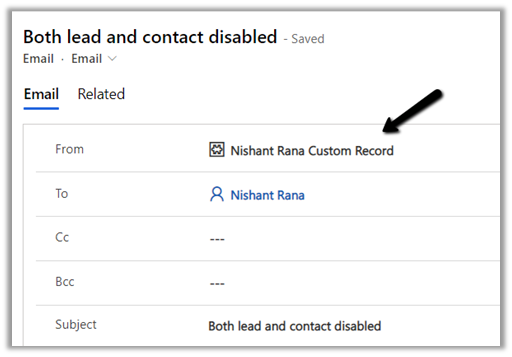
Now let us try the same by disabling this custom record as well i.e. now we have all the matching records lead, contact, and the custom entity one disabled.
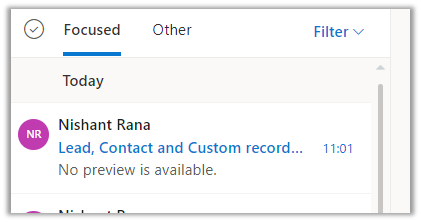
Result – As no matching record was found it creates it against an email and highlights it in red.
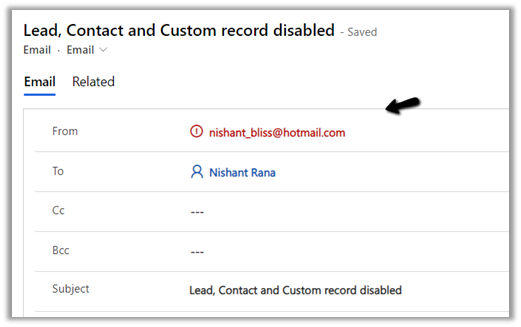
It is tracked the email even though the record were inactive.
Now let us delete that inactive contact record and send the same mail from the same account. We have the create contact option enabled right now.
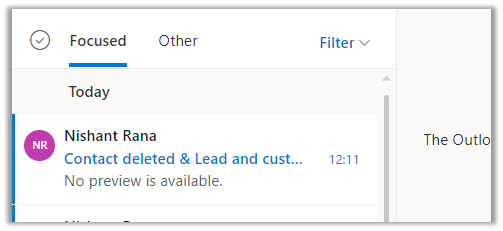
Result – The mail was tracked but no contact record was created.
- Now let us delete the matching inactive lead record from CRM, and keep the matching inactive custom entity record as it is.

Result – Now as we do not have any lead or contact record, the email as expected is not tracked as we have opted for tracking – Email messages from leads, contact, and accounts.
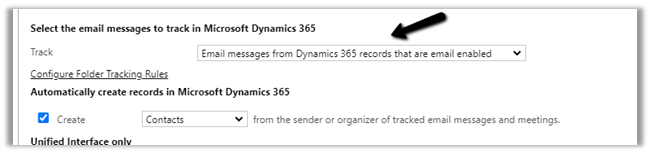
- Let us change the tracking option to Email messages from Dynamics 365 records that are email enabled – In this case, all email messages will be tracked for those entities having email-enabled (including custom entities)
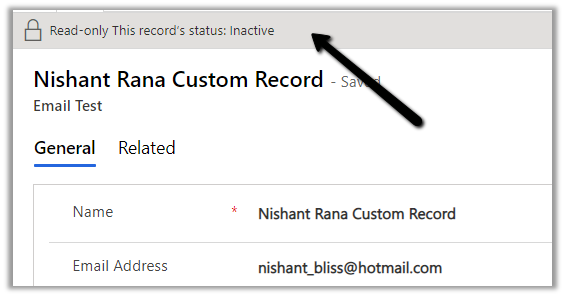
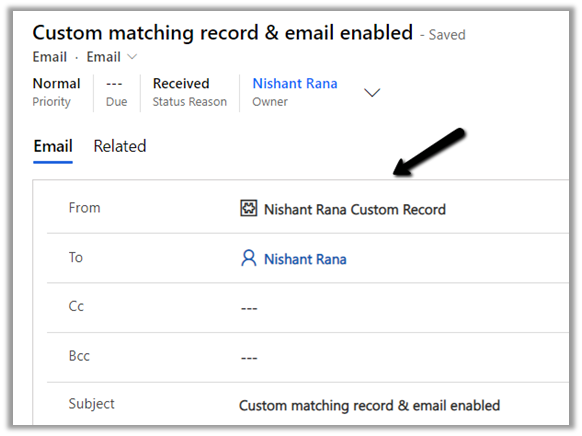
We can see the email tracked even though the custom matching record is inactive.
- Now let us set the tracking option as Email messages in response to Dynamics 365 email
This will track replies or forwards of email messages that have already been tracked.
Let us send a new mail, we only have an inactive matching custom entity record in CRM right now.
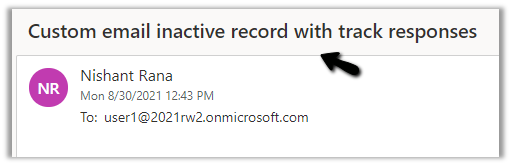
As expected the email is not traced as it is a new email, not a response.
- Let us send another email, this time we have created a matching contact record in CRM.
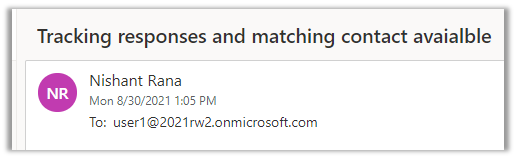
As expected the emails are not tracked as they are not the responses.
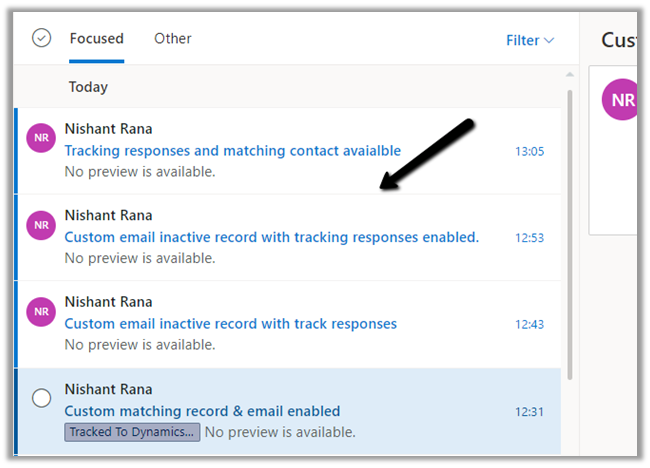
- Now let us respond to an existing tracked email.
Reply Sent From Outlook :

Reply From within CRM :
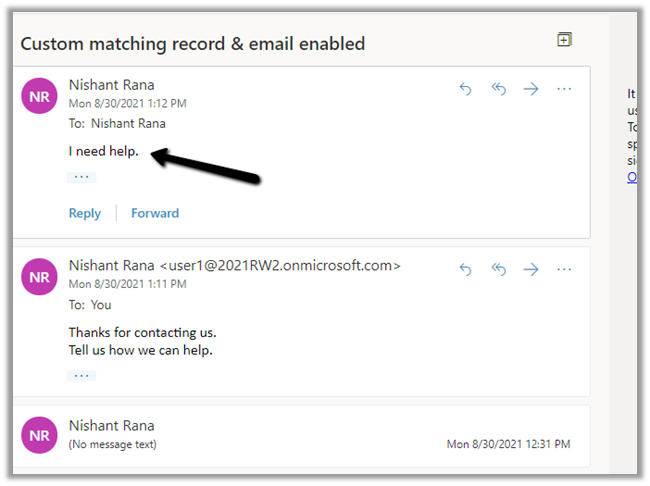
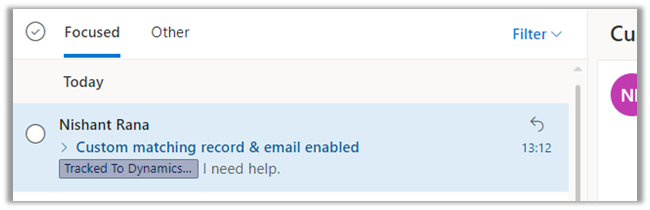
We can see it tracked in CRM.
- And finally the last option No email messages is self-explanatory

In a nutshell –
| Tracking | |
| All Email Messages | Email tracked, email activity created.
If an existing contact record is found, it is associated. If no contact record is found, it will be created if Create contact record option is enabled. Here if for Create Option we have selected Lead then lead will be created instead. If no existing record is found and create contact is disabled, then it is associated with an unknown email address (marked as red) If both matching lead and contact records are found, then the contact record is associated with the email activity. |
| Email messages from Dynamics 365 Lead, Contact, and Account | The email from only matching lead, contact, or account will be tracked.
Even if the matching record is disabled, the email is tracked. Here even if the create option is enabled, no lead or contact records are created. |
| Email messages from Dynamics 365 records that are email enabled. | It considers all the entities with email enabled not just lead, contact and account. |
| Email messages in response to Dynamics 365 email | Only replies or forwards of email messages that have been already tracked will be considered for tracking. |
| No email messages | No email messages are tracked. |
Check the details here –
Hope it helps..