Recently we noticed File usage of some of our environments reaching around 50 GB, and most of it was because of the AsyncOperation table.

So to quickly delete the AscyncOperation records the option we can choose is –
Create a new Bulk Record Deletion job from Settings >> Data Management

Select System Jobs table and filter as System Job Type equals Workflow

Select Bulk deletion job start time as Immediately
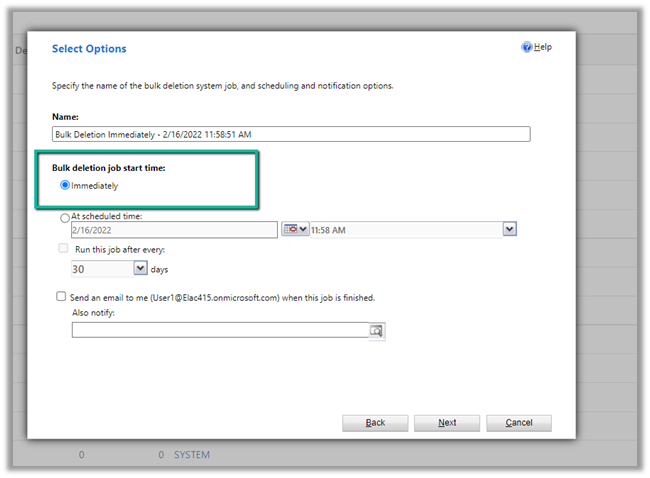
The Immediately option will only be available –
- For entity – System Jobs
- Filter Criteria is System Job type equals Workflow (we can add additional criteria)
- User has organization-level
delete rights on AsyncOpertion entity.
This will only delete the AsyncOperation records that are in the completed state of system job type workflow.
It will delete 1 million records whenever it is run. If there are more than 1 million records, it will have to be run again.
The key part is that it will delete the records through direct SQL Execution, so the records will be deleted immediately, rather than each record going through the delete pipeline, thus improving the performance immensely.
Back to our bulk deletion job, we can click on Submit to initiate the deletion.

We encountered a few errors when submitting, the solution was to keep trying, and eventually it will get submitted successfully.

After successful submission, we can see all our completed workflow system job records deleted immediately.
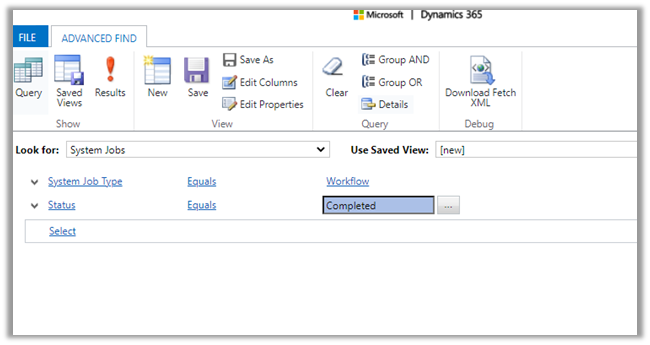
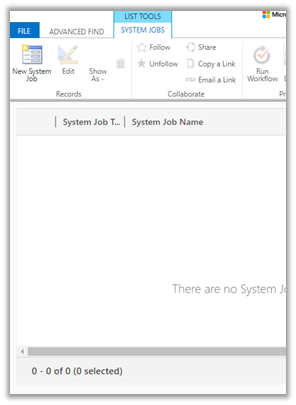
Also as it is Sync Job, we will not see it listed in Bulk Record Deletion views.
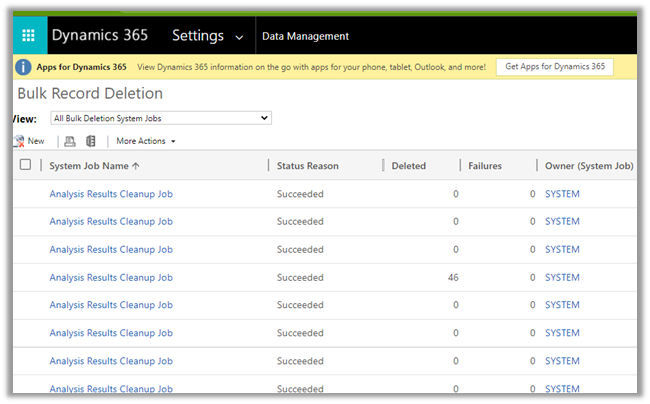
Get more details here –
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/power-platform/admin/free-storage-space#reduce-file-storage
Hope it helps..