We can define the Custom API’s binding type as Global, Entity, or Entity Collection. In this post, we can see how a Global and Entity binding type Custom API can be defined, write a corresponding plugin, and then invoke/test through Postman.
We can create Custom API through Plugin Registration Tool, Power Apps, Code, Solution files, and or can use XrmToolBox Plugin – Custom API Manager.
Below we have defined a Custom API name custom_GlobalAPI, with binding type as Global and one Request (input) parameter and Response (output) Property of type string.

Below is how we define the plugin type for it and can access the input and output parameters through context.

To test it we can use the XrmToolBox Custom API Tester plugin as shown below

And from Postman, once we have the access token, we can call the Custom API as shown below.

Now for a Bound Custom API, we have the following definition. It is bound to the Contact table and has one input parameter and one output parameter similar to our Global Custom API.
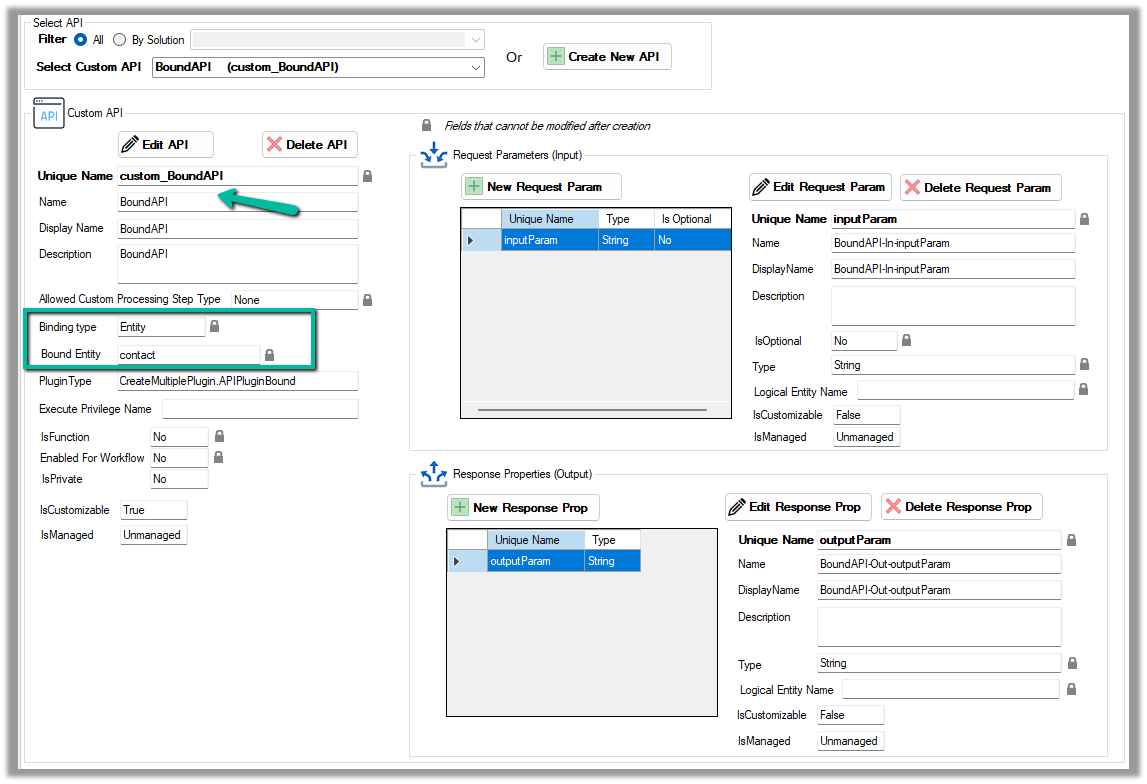
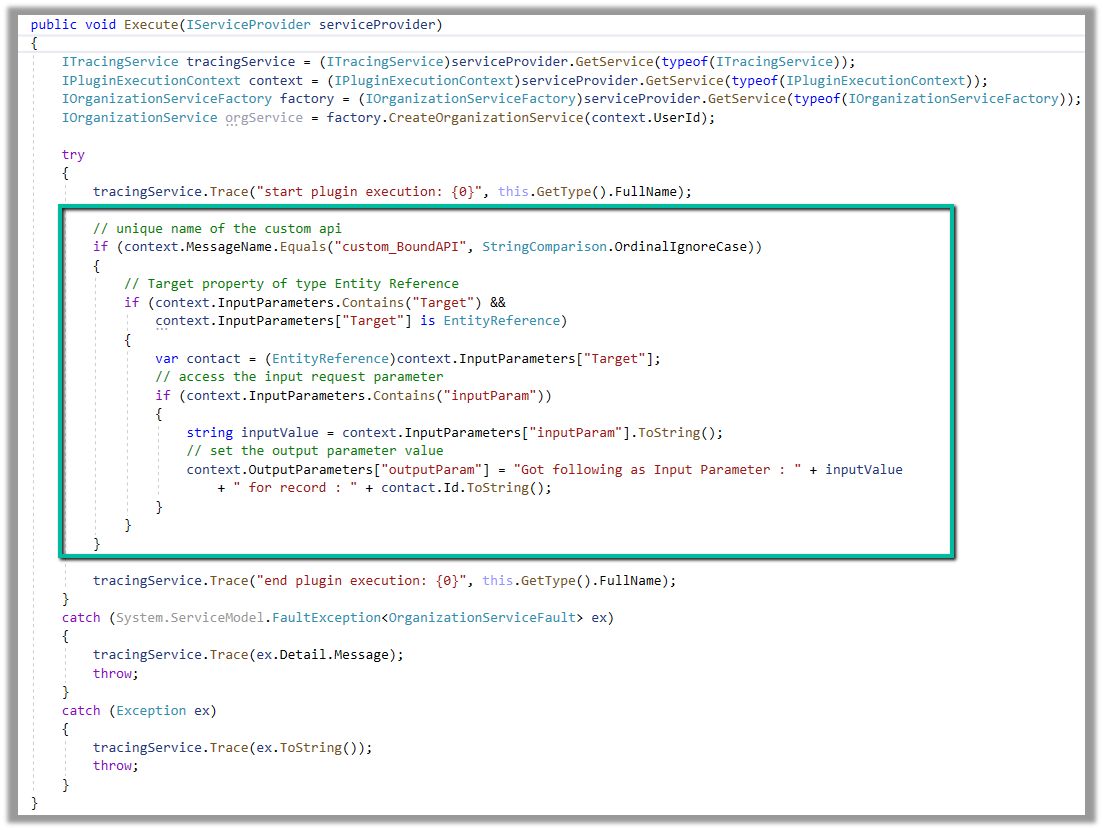
Below is how we define the plugin type for it, and can access the input and output parameters similar to Global Custom API.
However, in the case of binding type Entity, we will have the Request parameter named Target of type Entity Reference for the bound entity added automatically.
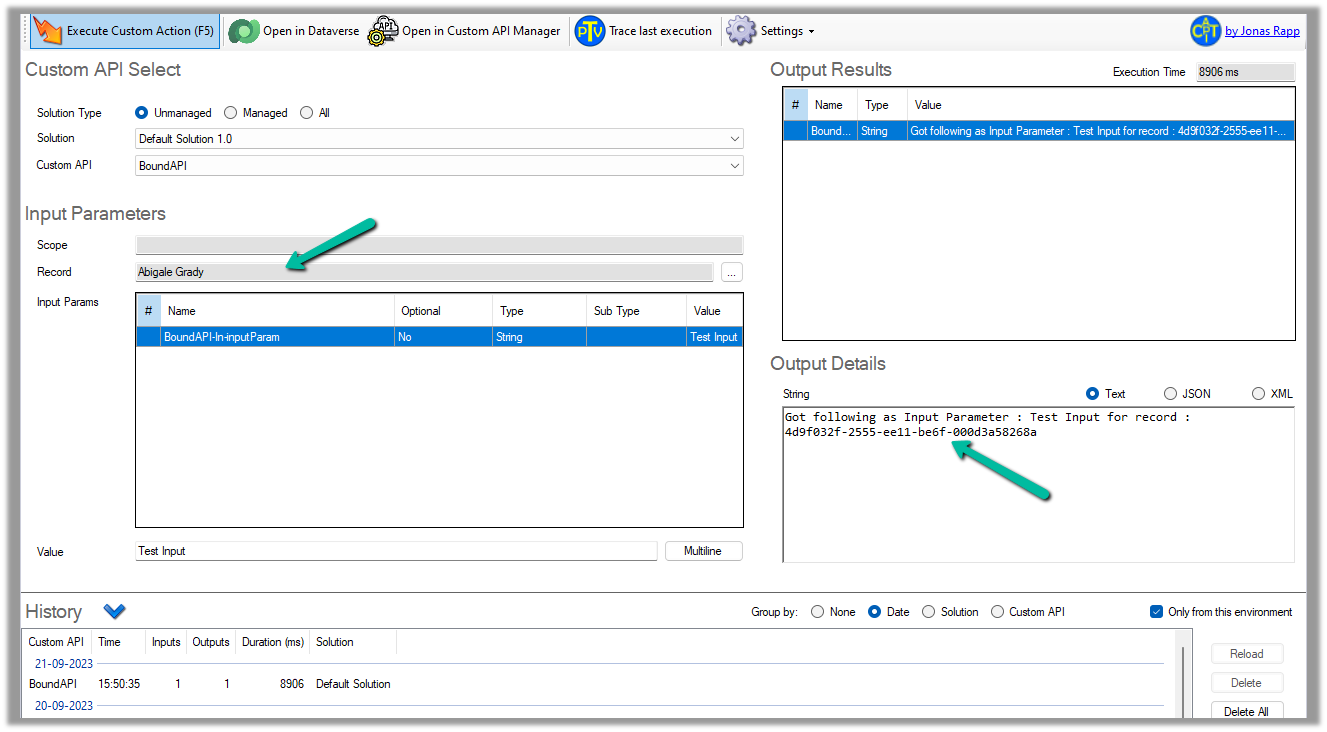
We can test it using the Custom API Tester plugin, however as it is bound type, we need to select/specify the contact record (the table it is bound to), before we can execute it.
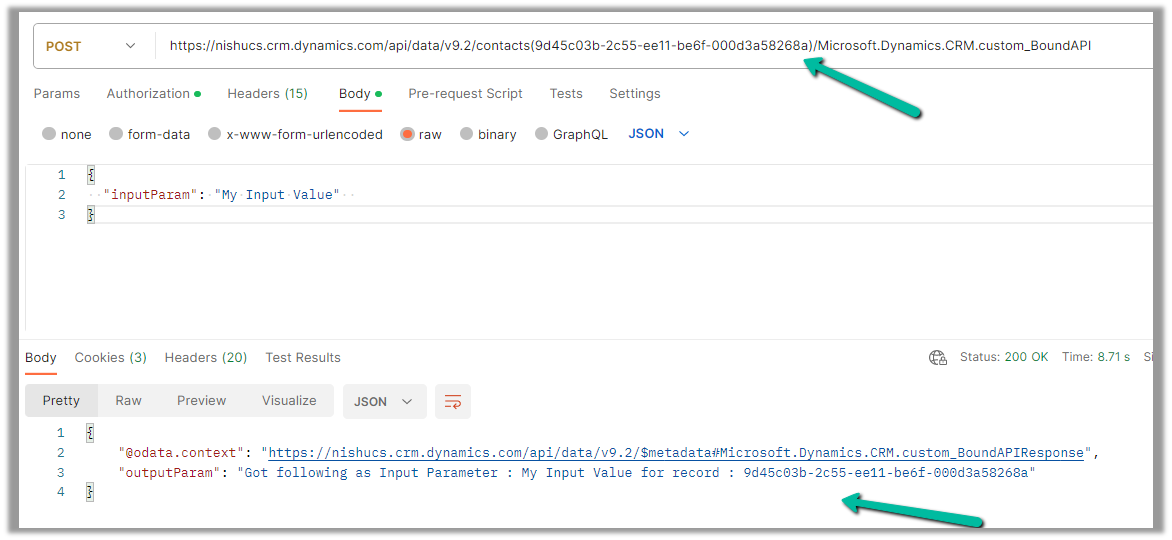
To call it from Postman, we need to use the fully qualified name i.e. Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.[unique name of the Custom API] unlike Global one.
public class APIPluginGlobal : IPlugin
{
public void Execute(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
ITracingService tracingService = (ITracingService)serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(ITracingService));
IPluginExecutionContext context = (IPluginExecutionContext)serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(IPluginExecutionContext));
IOrganizationServiceFactory factory = (IOrganizationServiceFactory)serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(IOrganizationServiceFactory));
IOrganizationService orgService = factory.CreateOrganizationService(context.UserId);
try
{
tracingService.Trace("start plugin execution: {0}", this.GetType().FullName);
// check for the message name i.e. Unique Name of the Custom API
if (context.MessageName.Equals("custom_GlobalAPI", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
// check for the request parameter in the inputparamters of the context
if (context.InputParameters.Contains("inputParam"))
{
// get the value of the input parameter
string inputValue = context.InputParameters["inputParam"].ToString();
// set the value of response property through outputparameters
context.OutputParameters["outputParam"] = "Got following value as Input : " + inputValue;
}
}
tracingService.Trace("end plugin execution: {0}", this.GetType().FullName);
}
catch (System.ServiceModel.FaultException<OrganizationServiceFault> ex)
{
tracingService.Trace(ex.Detail.Message);
throw;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
tracingService.Trace(ex.ToString());
throw;
}
}
}
public class APIPluginBound : IPlugin
{
public void Execute(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
ITracingService tracingService = (ITracingService)serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(ITracingService));
IPluginExecutionContext context = (IPluginExecutionContext)serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(IPluginExecutionContext));
IOrganizationServiceFactory factory = (IOrganizationServiceFactory)serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(IOrganizationServiceFactory));
IOrganizationService orgService = factory.CreateOrganizationService(context.UserId);
try
{
tracingService.Trace("start plugin execution: {0}", this.GetType().FullName);
// unique name of the custom api
if (context.MessageName.Equals("custom_BoundAPI", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
// Target property of type Entity Reference
if (context.InputParameters.Contains("Target") &&
context.InputParameters["Target"] is EntityReference)
{
var contact = (EntityReference)context.InputParameters["Target"];
// access the input request parameter
if (context.InputParameters.Contains("inputParam"))
{
string inputValue = context.InputParameters["inputParam"].ToString();
// set the output parameter value
context.OutputParameters["outputParam"] = "Got following as Input Parameter : " + inputValue
+ " for record : " + contact.Id.ToString();
}
}
}
tracingService.Trace("end plugin execution: {0}", this.GetType().FullName);
}
catch (System.ServiceModel.FaultException<OrganizationServiceFault> ex)
{
tracingService.Trace(ex.Detail.Message);
throw;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
tracingService.Trace(ex.ToString());
throw;
}
}
}
Hope it helps..
Discover more from Nishant Rana's Weblog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.



One thought on “Dataverse Custom API – Global and Entity (Binding Type) example”