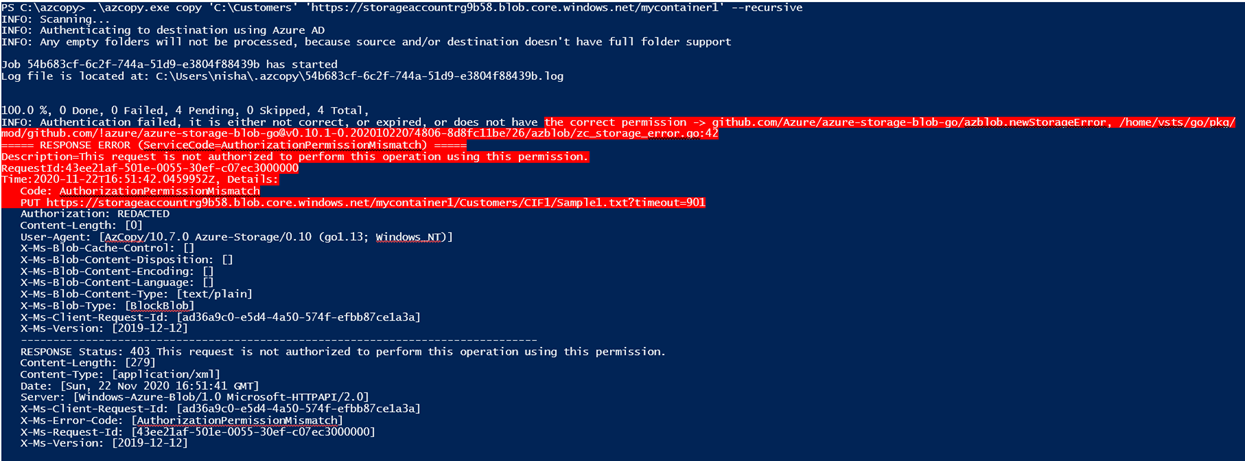
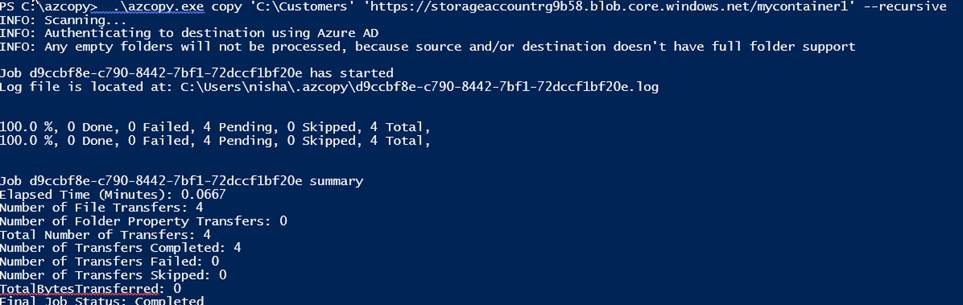
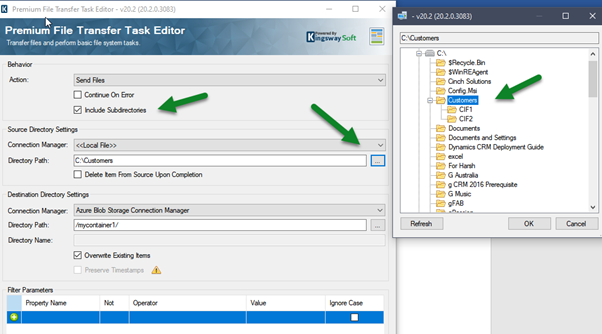
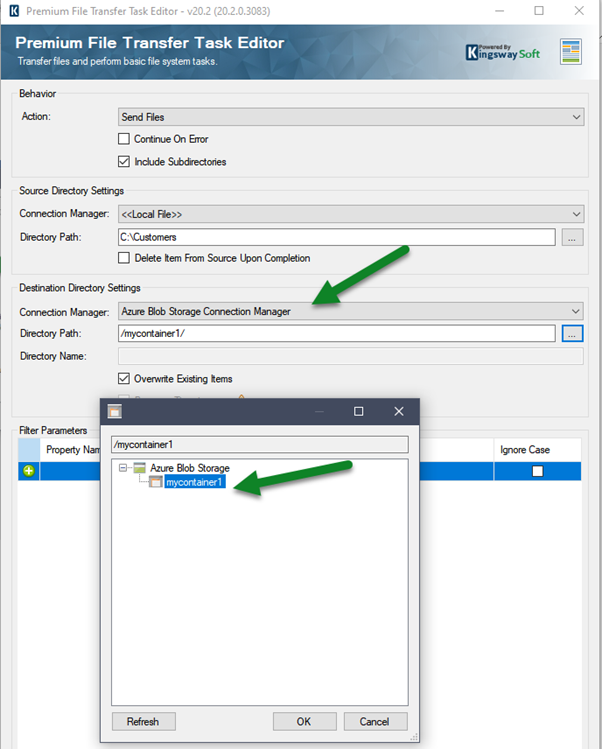
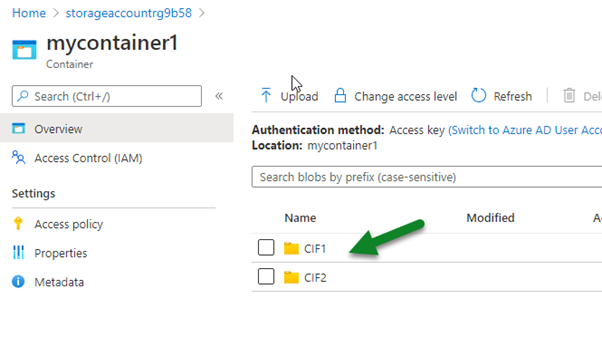
Always Encrypted is used for encryption at the column level rather than the entire database. It provides both data at rest as well in memory (in flight).
It is different from column (cell-level) and Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) which uses keys and certificates, which are stored in the database. In the case of Always Encrypted, keys are managed outside the database. SQL Server cannot decrypt on its own, as it is the client who encrypts / decrypts on the fly, separating those who own the data from the one who manages it.
To enable Always Encrypted we can use either T-SQL or the Always Encryption Wizard in SSMS. It supports both Randomized and Deterministic Encryption types.
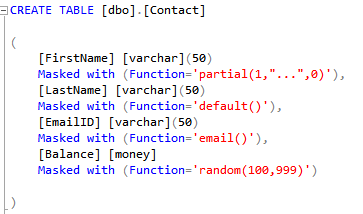
- Columns are encrypted using CEK – Column Encryption Key.
- The encrypted versions of each CEK are stored in the database.
- CMK – Column Master Key is used to encrypt all the CEKs.
- Only the client possesses the CMK which is stored in either Azure Key Vault, Certificate Store, HSM.
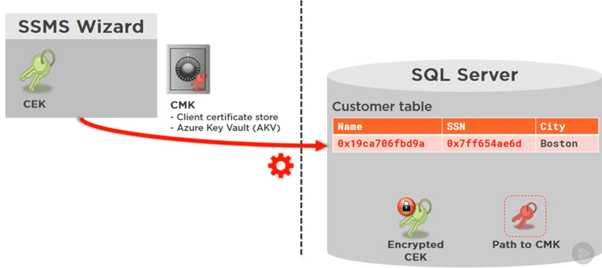
SSMS Wizard generates both CEK and CMK. CMK is stored in the Client certificate or Azure Key Vault.
CMK is used to encrypt CEK. The encrypted CEK along with Path to CMK is what is stored in the database. So, the database has no way of decrypting the data.
Next SSMS Wizard begins the encryption process, where it creates a new temporary table, transfers the data from the table and encrypts it on the fly, and then drops and replaces the main table.
All of this occurs on the fly at the client side which is SSMS in this case.

The client will pass the ‘Column Encryption Setting=Enabled’ in the connection string, which fetches the Encrypted CEK and Path to CMK from the database.
The client uses the Path to CMK to get the CMK and uses it to decrypt the encrypted CEK received and then uses the CEK to decrypt the encrypted data.
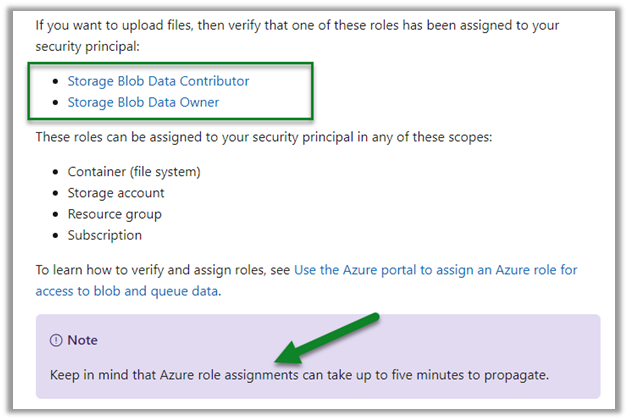
To apply Always Encrypted, within SSMS, right-click the database and select Tasks > Encrypt Columns…
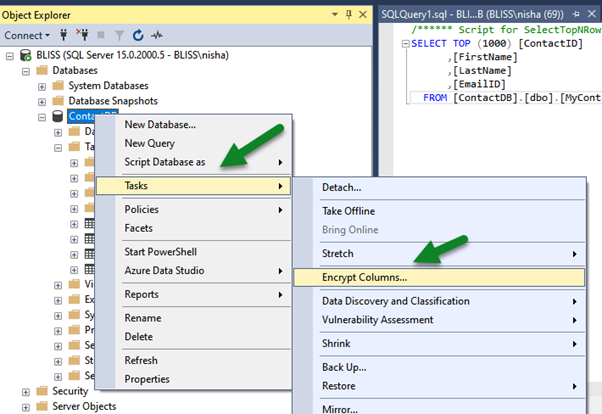
Below we have selected the Email Id column of MyContact table.

The below wizard step is used for generating CMK which can be either stored in Windows Certificate Store or Azure Key Vault with the client.

We can either run the encryption at that time or choose to generate a PowerShell Script which we can run later.
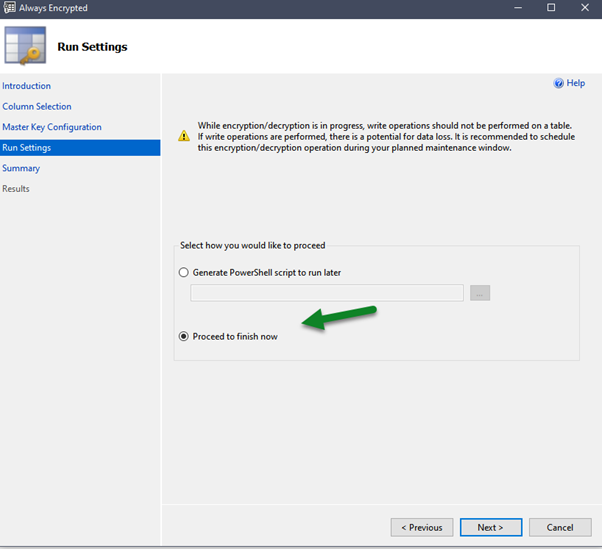
Below is the summary of steps that will be performed



To decrypt here, at the client which is our SSMS in this case, right-click in the query window and select Connection > Choose Connection…
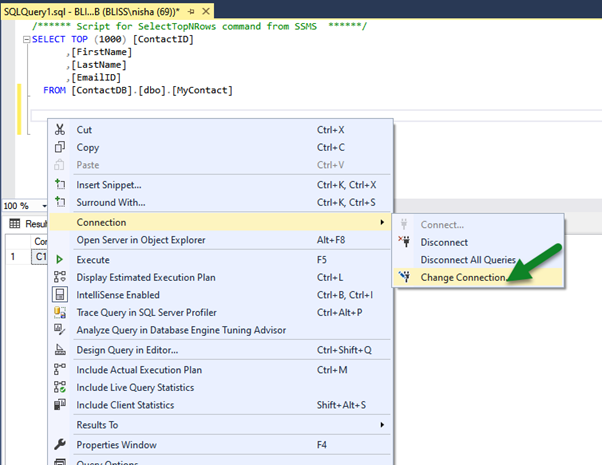
Specify column encryption setting=enabled in the Additional Connection Parameters tab.


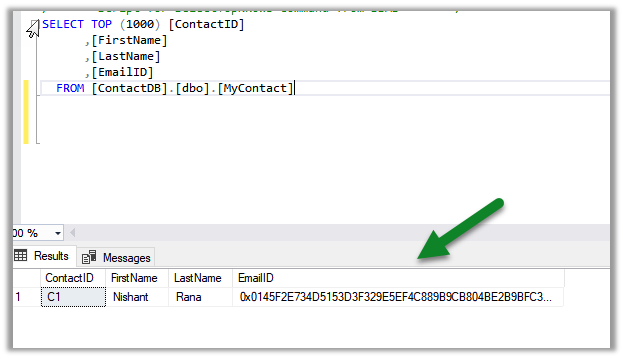
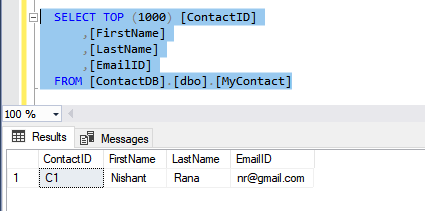
We can see the actual data as the client SSMS in this case, peforms the decryption at the run time using the path to CMK and encrypted CEK details received from the database.
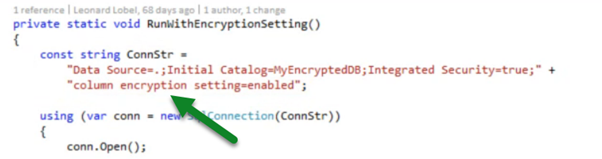
- Usage within a console application –
Few points to consider while planning to use Always Encrypted –
https://www.sentryone.com/blog/aaronbertrand/t-sql-tuesday-69-always-encrypted-limitations
Reference – Pluralsight – SQL Server Course
Hope it helps..