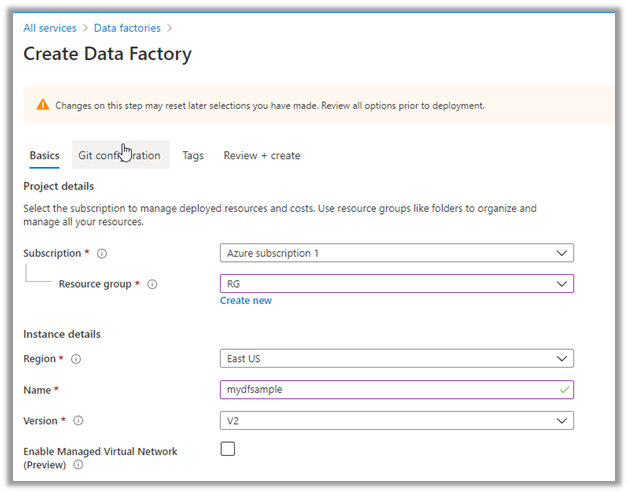
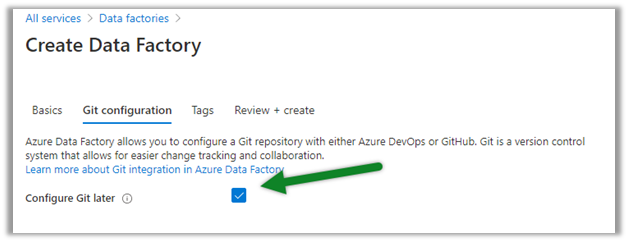
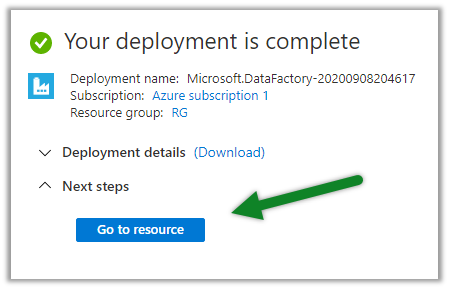
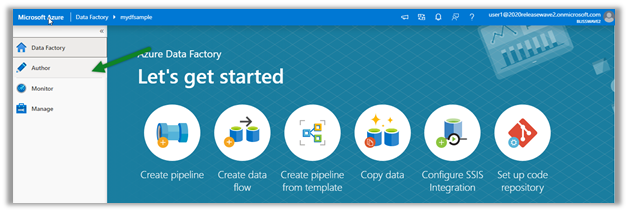
Cloud Computing enables companies to consume a complete resource – such as virtual machine, storage, or an application as a utility – just like electricity – rather than having to build and maintain computing infrastructure in-house.
Cloud provider provides the cloud infrastructure which is shared across multiple clients. Clients can select which service to use and only need to pay for that service, which is billed on-demand.
Cloud provider takes care of high availability (disk failure, power supply) and disaster recovery (natural or human disaster like fire, flood, etc.)
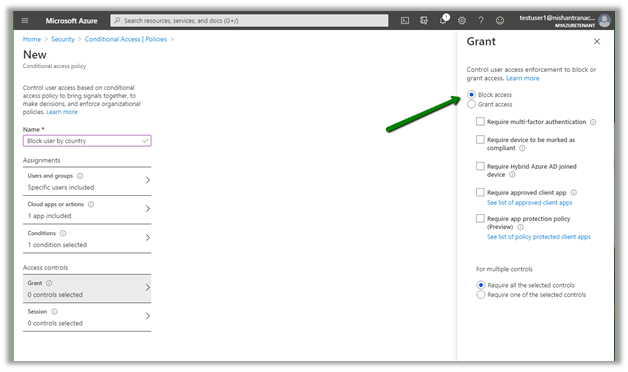
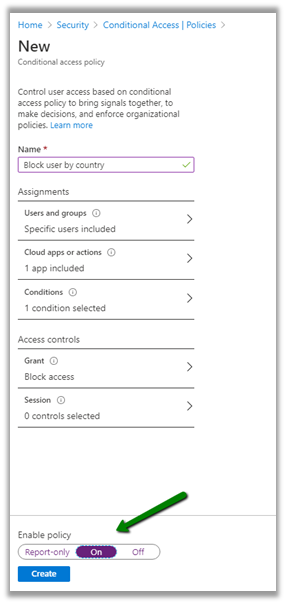
Advantages of using cloud computing
Rapid elasticity, only pay for the services used, reliability, economics of scale, etc.
Azure Regions Interactive Map
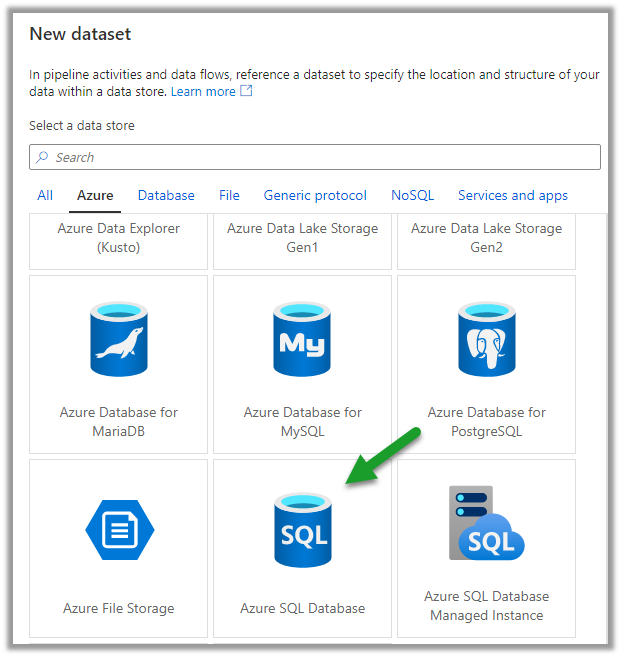
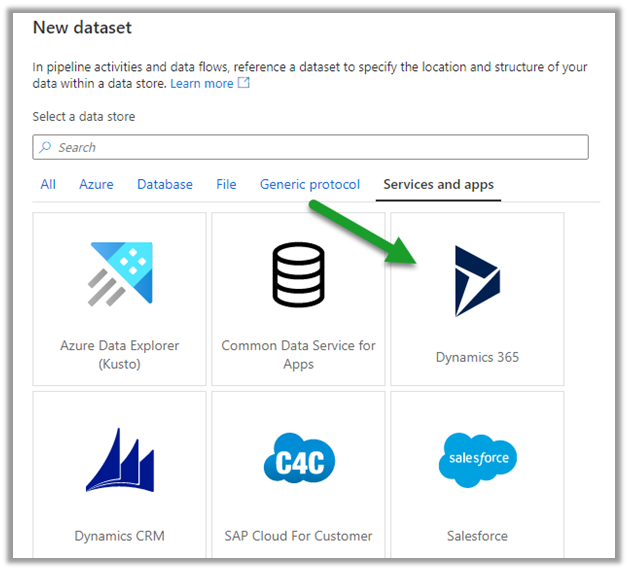
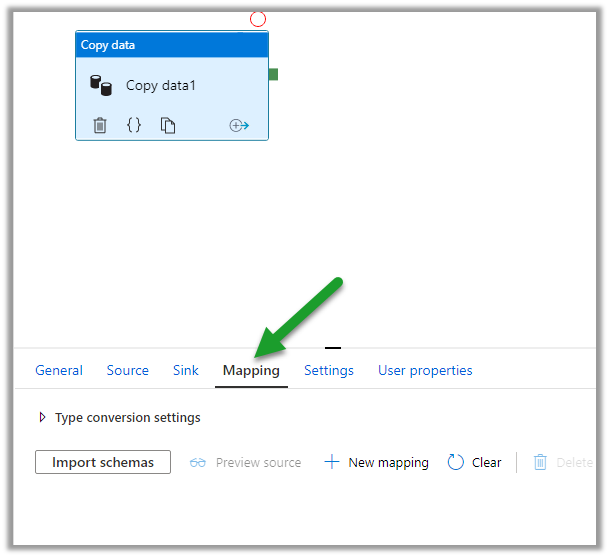
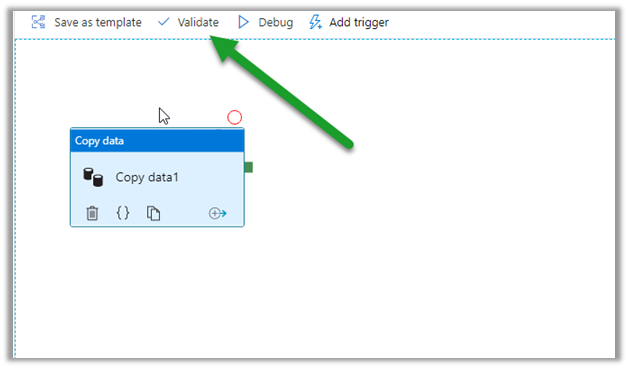
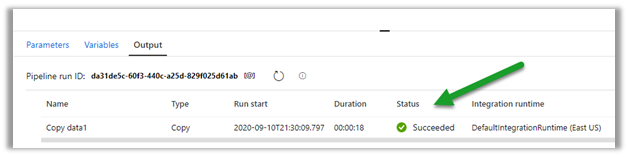
Types of Cloud Computing Services.
- IaaS – Infrastructure as a service – Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Storage.
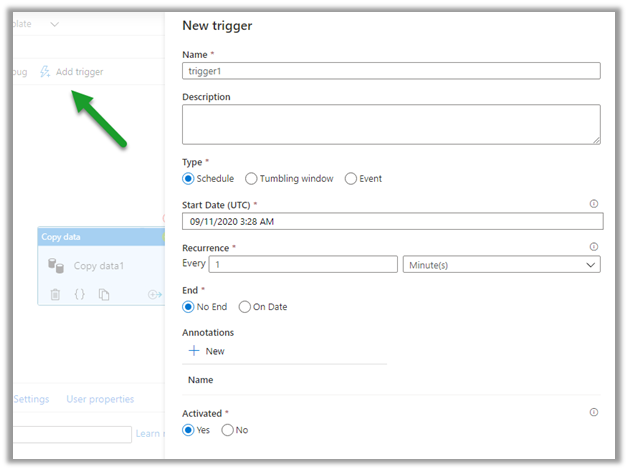
- PaaS – Platform as a service – Azure Functions, Logic Apps, Azure Automation.
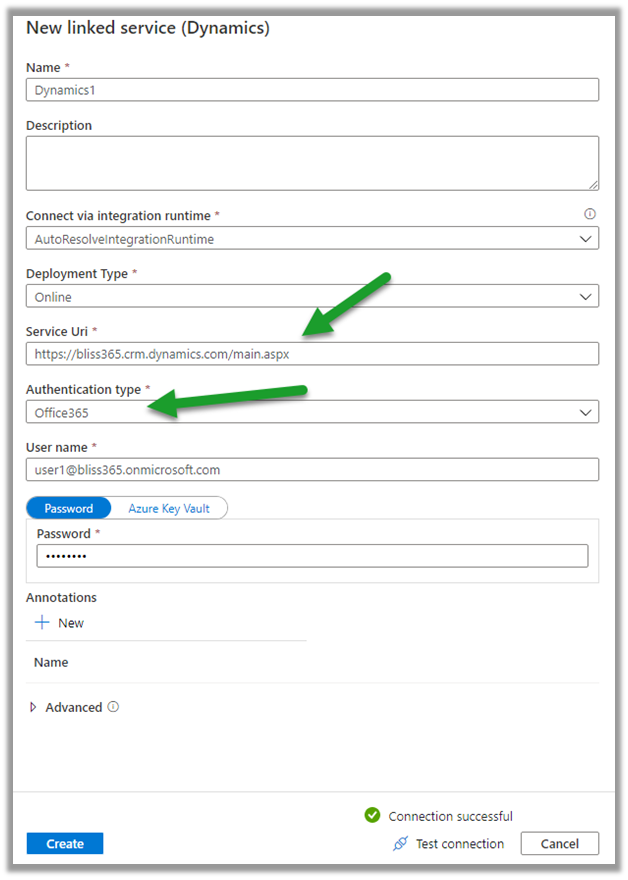
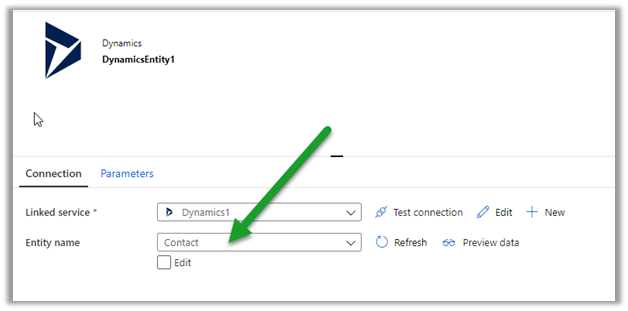
- SaaS – Software as a service – Dynamics 365, SharePoint, Power Platform.

Types of Cloud computing deployment models.

Hope it helps..